Assessing the circular re-design of prefabricated building envelope elements for carbon neutral renovation
Buildings and the construction industry at large are significant contributors to the catastrophic climate breakdown. The built environment is responsible for 37% of the total global carbon emission, of which about a third arises from the energy used to produce building and construction materials, usually referred to as embodied carbon. One of the key strategies to reduce the environmental impact of buildings is to significantly improve their energy efficiency, which is referred to as deep renovation. Prefabricated building envelope elements intended to prevent heat loss through the building envelope are considered a key deep-renovation technology. Connecting prefabricated elements to a building reflects a potential stream of waste if applied linearly with severe negative environmental impact in terms of natural resource depletion and exposure to pollutants. This article reports on a quantitative Design for Disassembly (Dfd) indicator to assess future recovery potential and, subsequently, its impact on embodied carbon emission of the circular redesign of three different prefabricated building envelope elements. Although none of the redesigned elements are yet considered 100% circular, the development of these three prefabricated building envelope elements showcases that the environmental impact can be substantially reduced following a well-structured and dedicated innovation process. The reduction of the environmental impact is indicated by lower quantities of embodied carbon up to 50% and an improved design for disassembly, reflecting a higher reuse potential of building materials and components. Several limitations and directions for further research were identified to advance the development of circular, prefabricated deep-renovation building envelope elements.
What was the DRIVE 0 project about? A full publishable report on the project’s results
«DRIVE 0 – Driving decarbonization of the EU building stock by enhancing a consumer centred and locally based circular renovation process»
The DRIVE 0 project deals with the promotion of strategies for the decarbonisation of the existing building stock through the implementation of deep renovation interventions. The project aims at promoting the adoption of a circular approach in renovation processes that, in order to be attractive and effective, must be based on the customer’s actual needs.
According to the DRIVE 0 approach, circular retrofitting is based on the use of energy from renewable sources and the use of materials from biological or technical cycles, in which waste production is minimised and end-of-life strategies with a positive impact on the environment are envisaged.
LIFE Buildupspeed
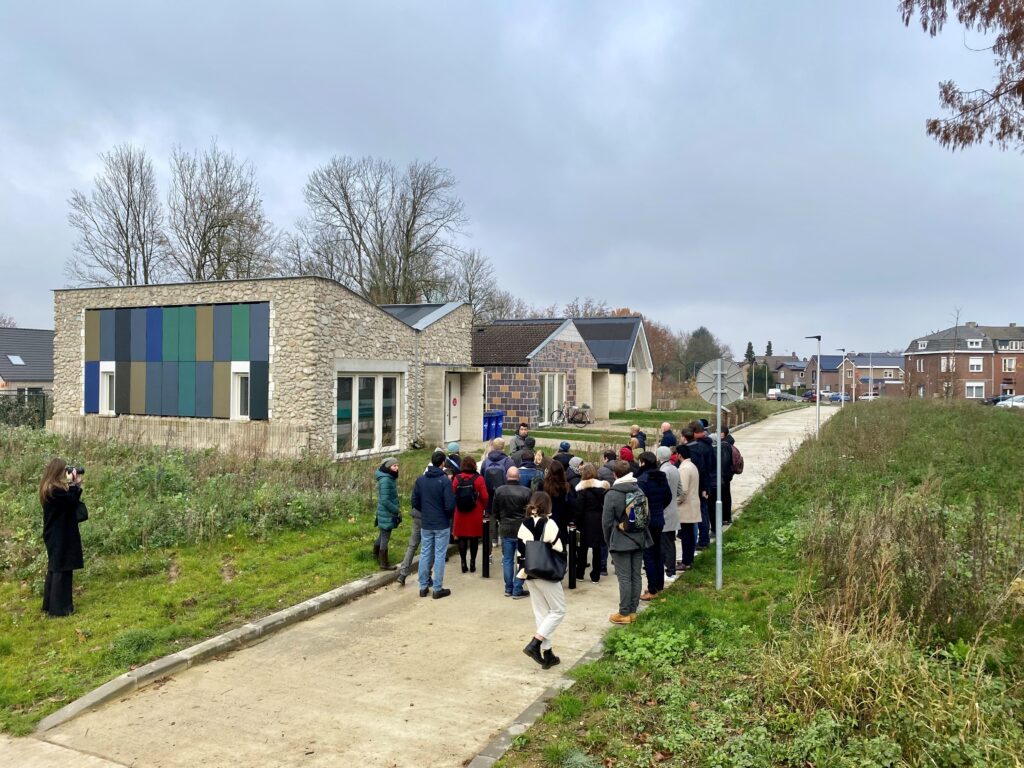

BuildUPspeed bouw voort BuildUPspeed bouwt voort op en kapitaliseert de resultaten en uitkomsten van relevante en gerelateerde H2020-projecten op het gebied van grondige renovatie, met name projecten en acties op het gebied van prefabricage, BIM-aanpassing voor renovatie en industrie 4.0. Bovendien zal BuildUPspeed ook de aanpak en netwerken van verschillende hoofdstukken van de ‘Energiesprong’ en […]
Mooi/SFEER
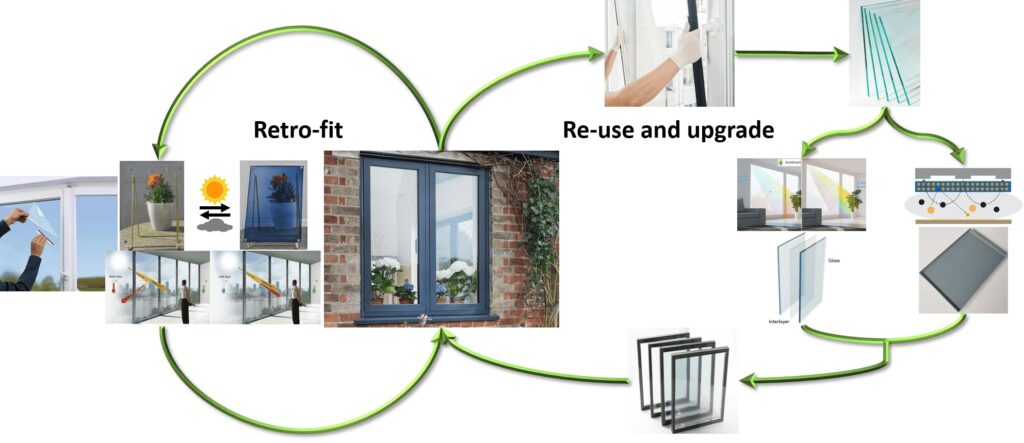
Slimme Folies en Circulaire Ramen voor Energie Efficiënte De bouwsector is verantwoordelijk voor ongeveer een derde van het totale energieverbruik en de CO2-uitstoot in Nederland. Voor gebouwen zijn de ramen een van de meest kwetsbare onderdelen met betrekking tot energieverlies. De huidige ramen in gevels in Nederland bestaan voornamelijk uit laagwaardige systemen welke niet meer […]
Environmental impact evaluation of energy saving and energy generation: case study for two Dutch dwelling types Building and Environment
The existing building stock is a logical target to improve the level of sustainability of the built environment by energy saving measures. These measures typically entail a decrease of operational energy demand, mainly by adding building components such as insulation packages and energy generating devices. Consequently, material related environmental impact might create a collateral disproportionate […]
Comparative performance assessment of a non-ventilated and ventilated BIPV rooftop configurations in the Netherlands Solar Energy.
Backside ventilation is one of the most common passive cooling methods of PV modules in the built environment, but might be under constraint when integrating PV in the building envelope. To investigate the short and long term effect of backside ventilation on Building Integrated PV (BIPV) performance and lifespan, a comparative BIPV field test is […]
Advanced light management techniques for two-terminal hybrid tandem solar cells
Multi-junction solar cells are considered for various applications, as they tackle various loss mechanisms for single junction solar cells. These losses include thermalization and non-absorption below the band gap. In this work, a tandem configuration comprising copper-indium-gallium-di-selenide (CIGS) and hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) absorber layers is studied. Two main challenges are addressed in this work. […]
Influence of the atmospheric species water, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide on the degradation of aluminum doped zinc oxide layers.
Aluminum doped zinc oxide (ZnO:Al) layers were exposed to the atmospheric gases carbon dioxide (CO2), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2) and air as well as liquid H2O purged with these gases, in order to investigate the chemical degradation behavior of these layers. The samples were analyzed by electrical, compositional and optical measurements before, during and after […]
Rolling Solar
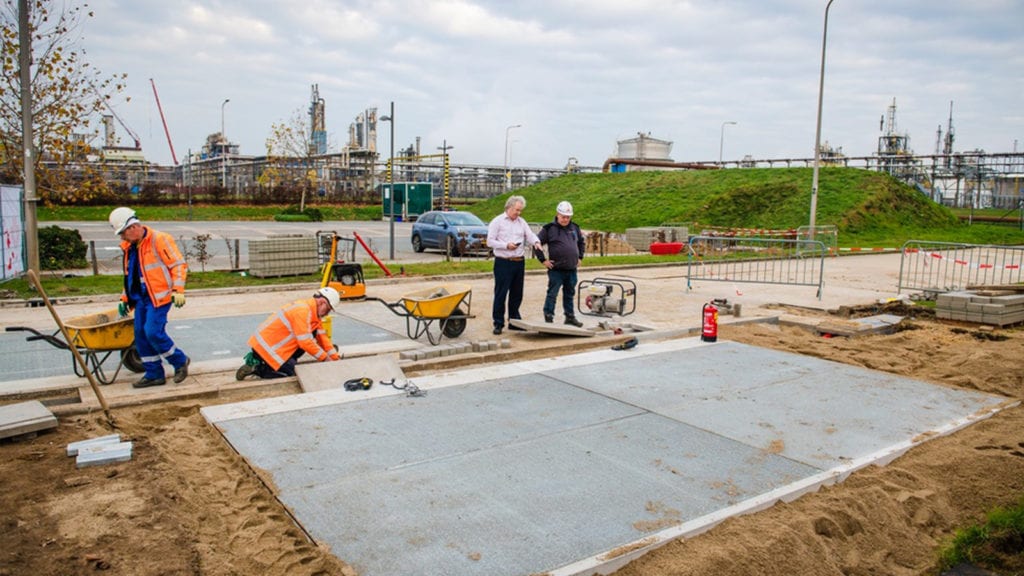

Stedelijke transformatie Engerietransitie Circulaire gebouwtechnologie Wat is het doel Looptijd Budget Subsidieprogramma en co-financiering Terug naar overzicht Samenwerkingspartners Onderzoekers Intern projectleider Zeger Vroon Team Fallon Colberts (Engineering) Jörgen Bouwmans (Engineering) Eric Hamers (Built Environment) Nieuws
H2020 Drive0
Het DRIVE 0-concept is gebaseerd op het ontwikkelen van circulaire oplossingen voor grondige renovatie en het ondersteunen van consumentgerichte bedrijfsmodellen voor 7 specifieke studie- en demonstratiecases als echte omgevingen. De geselecteerde cases zijn al in voorbereiding en elk van deze cases heeft een specifieke lokale drijfveer voor de behoefte aan een holistische en circulaire grondige […]
